INS LifeGuard
Understanding Blood Oxygen and Its Importance
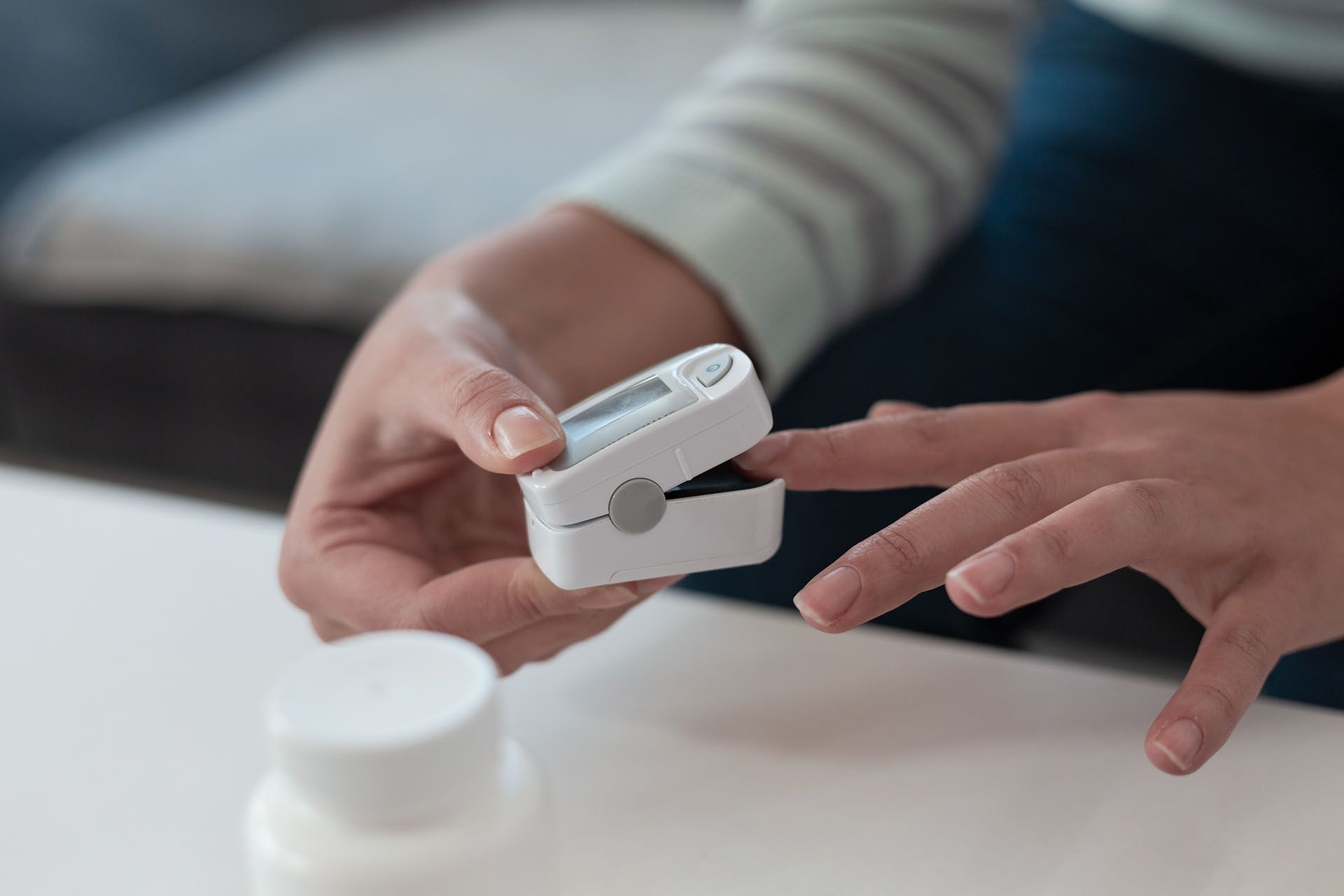

What is Blood Oxygen?
Blood oxygen refers to the amount of oxygen carried by red blood cells from the lungs to the rest of the body. Oxygen is essential for cellular metabolism, which is the process by which cells produce energy. The level of oxygen in the blood is a critical indicator of overall health and is measured using a device called a pulse oximeter. Normal blood oxygen levels typically range from 95% to 100%.
Why is Blood Oxygen Important?
Energy Production: Oxygen is crucial for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell. Without sufficient oxygen, cells cannot efficiently produce ATP, leading to decreased energy levels and impaired cellular function.
Brain Function: The brain is highly sensitive to changes in oxygen levels. Adequate oxygen supply is essential for maintaining cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and decision-making.
Immune System: Oxygen plays a key role in the functioning of the immune system. White blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections, require oxygen to function effectively.
Organ Function: All organs, including the heart, liver, and kidneys, rely on a constant supply of oxygen to function properly. Low oxygen levels can lead to organ dysfunction and failure.
Consequences of Low Blood Oxygen Levels
Low blood oxygen levels, also known as hypoxemia, can have serious health consequences. Hypoxemia can be caused by a variety of factors, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and environmental factors. Here are some potential consequences of low blood oxygen levels:
Shortness of Breath: One of the most immediate symptoms of low blood oxygen levels is shortness of breath. This occurs because the body is trying to increase oxygen intake by breathing more rapidly and deeply.
Fatigue: Low oxygen levels can lead to chronic fatigue as the body's cells struggle to produce enough energy. This can result in decreased physical and mental performance.
Cyanosis: Hypoxemia can cause a bluish discoloration of the skin, lips, and nails, known as cyanosis. This occurs because of the reduced oxygenation of the blood.
Cognitive Impairment: Prolonged hypoxemia can affect brain function, leading to confusion, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating. In severe cases, it can cause unconsciousness or coma.
Heart Problems: The heart has to work harder to pump oxygen-depleted blood, which can lead to arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), heart failure, and other cardiovascular issues.
Organ Damage: Chronic low oxygen levels can cause damage to vital organs. For example, the kidneys may suffer damage due to inadequate oxygen supply, leading to renal failure.
Increased Risk of Infections: Since the immune system relies on oxygen to function properly, low blood oxygen levels can weaken the immune response, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Monitoring and Managing Blood Oxygen Levels
Blood Oxygen Levels: From Normal to Dangerous
Blood oxygen levels are typically measured using a pulse oximeter, a non-invasive device that estimates the percentage of oxygen saturation in the blood (SpO2). These levels can range from normal to dangerously low, with specific thresholds indicating various states of health.
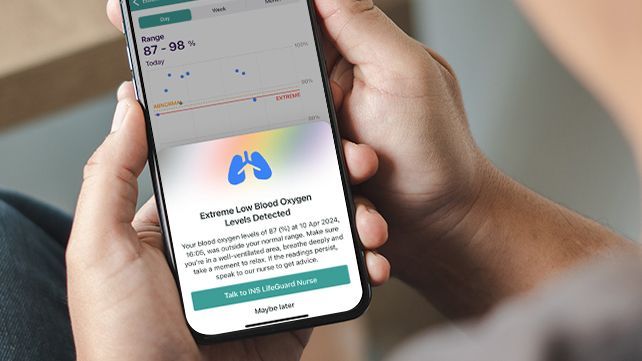
Understanding Blood Oxygen Saturation (Sp02)
Blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) is crucial for monitoring conditions related to low blood oxygen levels; normal levels range from 95% to 100%. However, dropping below 90% can swiftly harm vital organs like the brain, heart, and kidneys. Download our handy guide for more on oxygen saturation levels, their implications, and symptoms of low blood oxygen saturation.

Normal Blood Oxygen Levels
95% to 100%: This range is considered normal for healthy individuals. It indicates that the blood is carrying an adequate amount of oxygen to meet the body's needs.
Mild Hypoxemia
90% to 94%: This range indicates mild hypoxemia, which means there is a slight reduction in blood oxygen levels. While this might not cause immediate symptoms, it can be a sign of underlying health issues such as respiratory or cardiovascular problems. Individuals in this range should monitor their oxygen levels and seek medical advice if the condition persists or worsens.
Moderate Hypoxemia
80% to 89%: This range is considered moderate hypoxemia. Individuals may experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and confusion. Immediate medical attention is recommended to identify and treat the underlying cause, as prolonged moderate hypoxemia can lead to serious health complications.
Severe Hypoxemia
70% to 79%: This range indicates severe hypoxemia, a dangerous condition that requires urgent medical intervention. Symptoms can include severe shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin and lips). If blood oxygen levels drop to this range, emergency medical services should be contacted immediately.
Critical Hypoxemia
Below 70%: This range is critically low and life-threatening. Immediate emergency medical intervention is necessary. Symptoms are severe and can include extreme shortness of breath, inability to stay awake, and potential loss of consciousness. Without prompt treatment, critical hypoxemia can result in organ failure and death.
Factors Affecting Blood Oxygen Levels
Several factors can influence blood oxygen levels, including:
Lung Conditions: Diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pneumonia, and pulmonary fibrosis can impair the lungs' ability to oxygenate blood.
Heart Conditions: Heart diseases that affect the pumping efficiency can reduce the amount of oxygenated blood circulated throughout the body.
High Altitude: At higher altitudes, the lower oxygen pressure can reduce blood oxygen saturation, leading to hypoxemia.
Sleep Apnea: This condition causes intermittent interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to temporary drops in blood oxygen levels.
Anaemia: A low red blood cell count reduces the blood's capacity to carry oxygen, which can result in lower oxygen levels.
Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring of blood oxygen levels is especially important for individuals with known risk factors, such as chronic lung or heart conditions. Pulse oximeters provide a simple and effective way to track these levels at home. If readings consistently fall below normal ranges, medical advice should be sought to determine the appropriate course of action.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Blood Oxygen Levels
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can improve lung capacity and efficiency, enhancing overall oxygenation.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages lung tissue and reduces the efficiency of oxygen exchange.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants and iron can support the health of red blood cells and improve oxygen transport.
- Breathing Exercises: Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing can help increase lung capacity and improve oxygenation.
- Hydration: Keeping well-hydrated helps maintain the optimal function of the lungs and blood vessels.
Conclusion
Blood oxygen is a vital component of overall health, playing a crucial role in energy production, brain function, and the immune response. Low blood oxygen levels can lead to a range of serious health consequences, including respiratory distress, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and organ damage. Monitoring and managing blood oxygen levels through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and environmental adjustments are essential for maintaining good health and preventing complications associated with hypoxemia.
By understanding the importance of blood oxygen and the potential risks of low oxygen levels, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure their oxygen levels remain within a healthy range, thereby supporting overall well-being.
INS LifeGuard prioritises prevention and is Australia's only nurse-on-call personal and medical alarm monitoring service. We cater to diverse needs, from seniors to individuals focused on personal health, providing real-time vital sign tracking for patients by both family and healthcare professionals. Our Professional TeleHealth Monitoring and emergency response, managed by qualified nurses, ensures situations are attended to immediately.
Find out more about our services by calling 1800 636 040 or visiting our website www.inslifeguard.com.au

About
INS LifeGuard is the only 24/7 nurse on-call personal and medical monitoring in Australia. We provide monitoring technology for both in the home and on the go and can also monitor other provider's equipment. Our services are suitable for anyone wanting support to stay independent such as the elderly, those with medical conditions and disabilities plus enhancing safety and security for lone workers.
Related Articles

-
Visit our website here
I hope you enjoy reading this blog post
INS LifeGuard is the only nurse on-call personal and medical alarm service in Australia. If you would like more information about INS LifeGuards solutions, visit our website here.
I hope you enjoy reading this blog post.
INS LifeGuard is the only nurse on-call personal and medical alarm service in Australia. If you would like more information about INS LifeGuards solutions, visit our website
here.

INS LifeGuard is the only nurse on-call personal emergency response service in Australia. We have a commitment to healthcare innovation which includes personal alarms and medical alert solutions that make independence easier, safer and more enjoyable.
Our services support Seniors, Carers, Providers, NDIS Participants, Retirement Villages, DVA, Lone Workers and anyone that wants the security that help is a press of a button away.
LATEST POSTS
PO Box 485 Unanderra NSW 2526 Australia
INS LifeGuard
International Enquiries
INS CareCall supplies and monitors emergency response equipment and services, including hardware manufactured by Chiptech, Smart-Caller, SmartLink, and the LifeGuard L-Series Diallers.
Monitoring of alarms is provided through INS LifeGuard's unique Emergency Response Centre, which is the only personal alarm response centre staffed by qualified nurses. This is an important distinction.
Quicklinks
Supporting
PO Box 485 Unanderra NSW 2526 Australia
INS LifeGuard
International Enquiries












